다익스트라 알고리즘(Dijkstra Algorithm)
다익스트라 알고리즘(Dijkstra Algorithm)은 그래프에서 단일 출발점에서 모든 노드까지의 최단 경로를 찾는 알고리즘입니다.
동작 원리
- 출발 노드의 최단 거리를 0으로 설정하고 나머지 노드의 최단 거리를 무한대로 설정합니다.
- 최단 거리가 가장 짧은 노드를 선택합니다.
- 선택된 노드와 연결된 인접 노드의 거리를 계산해서 기존 거리보다 짧다면 업데이트합니다.
- 모든 노드를 방문하거나 더 이상 업데이트가 없을 때까지 위 단계를 반복합니다.
Java 코드 구현
import java.util.*;
class Dijkstra {
// 노드 클래스
static class Node implements Comparable<Node> {
int vertex;
int cost;
public Node(int vertex, int cost) {
this.vertex = vertex;
this.cost = cost;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node other) {
return this.cost - other.cost; // 비용 기준 오름차순
}
}
public static int[] dijkstra(List<List<Node>> graph, int start) {
int n = graph.size();
int[] distances = new int[n];
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
Arrays.fill(distances, Integer.MAX_VALUE); // 모든 거리를 무한대로 초기화
distances[start] = 0;
PriorityQueue<Node> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
pq.add(new Node(start, 0));
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
Node current = pq.poll();
int currentVertex = current.vertex;
if (visited[currentVertex]) continue;
visited[currentVertex] = true;
for (Node neighbor : graph.get(currentVertex)) {
int newDist = distances[currentVertex] + neighbor.cost;
if (newDist < distances[neighbor.vertex]) {
distances[neighbor.vertex] = newDist;
pq.add(new Node(neighbor.vertex, newDist));
}
}
}
return distances;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 6; // 노드 수
List<List<Node>> graph = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
// 그래프 정의 (노드1, 노드2, 비용)
graph.get(0).add(new Node(1, 4));
graph.get(0).add(new Node(2, 2));
graph.get(1).add(new Node(2, 5));
graph.get(1).add(new Node(3, 10));
graph.get(2).add(new Node(4, 3));
graph.get(4).add(new Node(3, 4));
graph.get(3).add(new Node(5, 11));
int start = 0; // 시작 노드
int[] distances = dijkstra(graph, start);
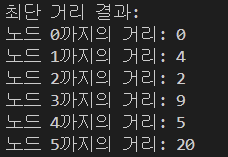
System.out.println("최단 거리 결과:");
for (int i = 0; i < distances.length; i++) {
System.out.println("노드 " + i + "까지의 거리: " + distances[i]);
}
}
}
구현 결과